Amr Ibn Sa'id on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Abū Umayya ʿAmr ibn Saʿīd ibn al-ʿĀṣ al-Umawī ( ar, عمرو بن سعيد بن العاص بن أمية الأموي; died 689/90), better known as al-Ashdaq (), was a member of
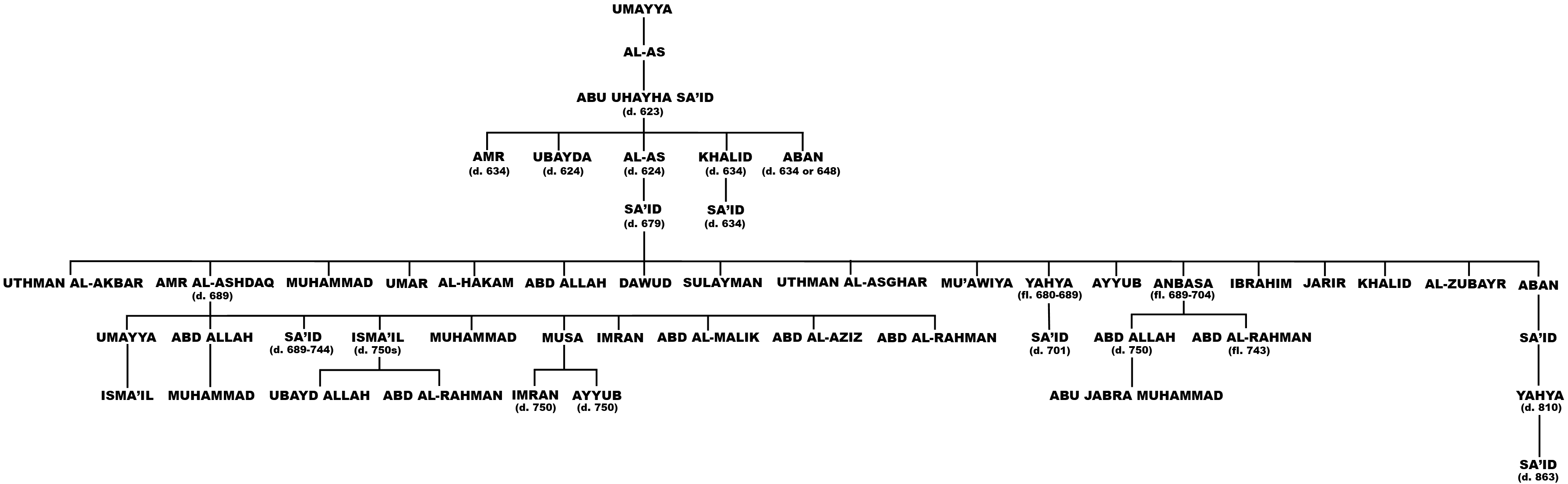 Al-Ashdaq's sons Umayya, Sa'id, Isma'il and Muhammad, all born to al-Ashdaq's wife Umm Habib bint Hurayth, were later reconciled with Abd al-Malik following the latter's victory over the Zubayrids in 692. Sa'id, who had participated in his father's revolt, subsequently migrated to Medina, then to
Al-Ashdaq's sons Umayya, Sa'id, Isma'il and Muhammad, all born to al-Ashdaq's wife Umm Habib bint Hurayth, were later reconciled with Abd al-Malik following the latter's victory over the Zubayrids in 692. Sa'id, who had participated in his father's revolt, subsequently migrated to Medina, then to
Banu Umayya
Umayyad dynasty ( ar, بَنُو أُمَيَّةَ, Banū Umayya, Sons of Umayya) or Umayyads ( ar, الأمويون, al-Umawiyyūn) were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of Al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In the ...
, general and a contender for the caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
al throne. He served as the governor of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
in 680, during the reign of Caliph Yazid I
Yazid ibn Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan ( ar, يزيد بن معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Yazīd ibn Muʿāwiya ibn ʾAbī Sufyān; 64611 November 683), commonly known as Yazid I, was the second caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate. He ruled from ...
() and later fought off attempts by the Zubayrid
Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam ( ar, عبد الله ابن الزبير ابن العوام, ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Zubayr ibn al-ʿAwwām; May 624 CE – October/November 692), was the leader of a caliphate based in Mecca that rivaled the ...
s to conquer Syria in 684 and 685 during the reign of Caliph Marwan I
Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya ( ar, links=no, مروان بن الحكم بن أبي العاص بن أمية, Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam ibn Abī al-ʿĀṣ ibn Umayya), commonly known as MarwanI (623 or 626April/May 685), was the fo ...
. His attempted coup against Caliph Abd al-Malik () in 689 ended with his surrender and ultimately his execution by Abd al-Malik himself.
Life
Amr was the son of theUmayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
statesman Sa'id ibn al-As
Saʿīd ibn al-ʿĀṣ al-Umawī () (died 678/679) was the Muslim governor of Kufa under Caliph Uthman () and governor of Medina under Caliph Mu'awiya I (). Like the aforementioned caliphs, Sa'id belonged to the Umayyad clan of the Quraysh.
...
and Umm al-Banin bint al-Hakam, the sister of another Umayyad statesman, Marwan ibn al-Hakam
Marwan ibn al-Hakam ibn Abi al-As ibn Umayya ( ar, links=no, مروان بن الحكم بن أبي العاص بن أمية, Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam ibn Abī al-ʿĀṣ ibn Umayya), commonly known as MarwanI (623 or 626April/May 685), was the fo ...
. He was nicknamed "al-Ashdaq" (the Widemouthed). When Sa'id died in 679, al-Ashdaq became the leader of this branch of the Umayyad clan. At the end of the reign of Caliph Mu'awiya I (), he was governor of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
but was then appointed the governor of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
at the accession of Caliph Yazid I
Yazid ibn Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan ( ar, يزيد بن معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Yazīd ibn Muʿāwiya ibn ʾAbī Sufyān; 64611 November 683), commonly known as Yazid I, was the second caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate. He ruled from ...
(). When the Umayyads were driven out of Mecca during the revolt of Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr in 682, al-Ashdaq was ordered by Yazid to send an army against the Zubayrids in the city. Al-Ashdaq appointed Ibn al-Zubayr's brother, Amr, to lead the expedition, but the force was defeated and Amr was executed by Ibn al-Zubayr. Toward the end of 683, al-Ashdaq was dismissed, Yazid died and was succeeded by his son, Mu'awiya II
Mu'awiya ibn Yazid ( ar, معاوية بن يزيد, Muʿāwiya ibn Yazīd; 664 – 684 CE), usually known simply as Mu'awiya II was the third Umayyad caliph. He succeeded his father Yazid I as the third caliph and last caliph of the Sufyanid ...
. The latter was ill and died a few months later, causing a leadership crisis in the Umayyad Caliphate, which saw most of its provinces recognize Ibn al-Zubayr as caliph.
When the pro-Umayyad Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
tribal nobility of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, chief among them the chieftain of Banu Kalb
The Banu Kalb ( ar, بنو كلب) was an Arab tribe which mainly dwelt in the desert between northwestern Arabia and central Syria. The Kalb was involved in the tribal politics of the eastern frontiers of the Byzantine Empire, possibly as early ...
, elected Marwan ibn al-Hakam as caliph at the Jabiya summit of 684, it was stipulated that Yazid's then-young son Khalid
Khalid (variants include Khaled and Kalid; Arabic: خالد) is a popular Arabic male given name meaning "eternal, everlasting, immortal", and it also appears as a surname.
would succeed Marwan, followed by al-Ashdaq. The latter commanded the right wing of Marwan's army during the Battle of Marj Rahit later that year, in which the Umayyads scored a resounding victory over the pro-Zubayrid Qays
Qays ʿAylān ( ar, قيس عيلان), often referred to simply as Qays (''Kais'' or ''Ḳays'') were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe does not appear to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic e ...
i tribes of Syria. During Marwan's expedition to wrest control of Egypt from its Zubayrid governor in 685, al-Ashdaq was present and delivered an address proclaiming Marwan's sovereignty from the pulpit of the mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
in Fustat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by t ...
. Afterward, al-Ashdaq was dispatched by Marwan to stave off an invasion of Palestine by Mus'ab ibn al-Zubayr
Muṣʿab ibn al-Zubayr ( ar, مصعب بن الزبير; died October 691) was the governor of Basra in 686–691 for his brother, the Mecca-based counter-caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr, during the Second Fitna. Mus'ab was a son of Zubayr ib ...
, who was attempting to conquer Umayyad Syria during Marwan's absence. He then joined Marwan and took up residence in the Umayyad capital of Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
. The caliph remained wary of al-Ashdaq's ambitions to the caliphate, particularly due to his popularity among the Syrian Arab nobility and his close kinship to Marwan, who was his maternal uncle and paternal relative as well. Marwan resolved to avoid the potential leadership bids of al-Ashdaq and Khalid by having his sons Abd al-Malik and Abd al-Aziz, in that order, recognized by the Syrian nobility as his chosen successors.
Abd al-Malik succeeded his father in late 685 but remained suspicious of al-Ashdaq. The latter did not relinquish his claims and viewed Abd al-Malik's accession as a violation of the arrangements reached in Jabiya. When the caliph left Damascus on a military campaign against Zubayrid-held Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
in 689, al-Ashdaq took advantage of his absence to launch a revolt, seize the city and declare his right as sovereign. This compelled Abd al-Malik to abandon his campaign and address al-Ashdaq's rebellion. In the ensuing standoff in Damascus between their supporters, Abd al-Malik offered al-Ashdaq amnesty in return for his surrender, to which al-Ashdaq obliged. However, Abd al-Malik remained distrustful of al-Ashdaq and had him summoned to his palace in Damascus, where he executed him in 689/90.
Family
 Al-Ashdaq's sons Umayya, Sa'id, Isma'il and Muhammad, all born to al-Ashdaq's wife Umm Habib bint Hurayth, were later reconciled with Abd al-Malik following the latter's victory over the Zubayrids in 692. Sa'id, who had participated in his father's revolt, subsequently migrated to Medina, then to
Al-Ashdaq's sons Umayya, Sa'id, Isma'il and Muhammad, all born to al-Ashdaq's wife Umm Habib bint Hurayth, were later reconciled with Abd al-Malik following the latter's victory over the Zubayrids in 692. Sa'id, who had participated in his father's revolt, subsequently migrated to Medina, then to Kufa
Kufa ( ar, الْكُوفَة ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Currently, Kufa and Najaf a ...
. He became a mentor of Khalid al-Qasri
Khālid ibn ʿAbdallāh al-Qasrī (; died 743) was an Arab who served the Umayyad Caliphate as governor of Mecca in the 8th century and of Iraq from 724 until 738. The latter post, entailing as it did control over the entire eastern Caliphate, mad ...
, who served as governor of Iraq in 724–738. Khalid's father Abdallah had been the head of al-Ashdaq's '' shurṭa'' (security forces). Sa'id was later reported to have visited the court of the Umayyad caliph Yazid II
Yazid ibn Abd al-Malik ( ar, يزيد بن عبد الملك, Yazīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik; — 28 January 724), also referred to as Yazid II, was the ninth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 9 February 720 until his death in 724.
Early life
Yazid was b ...
in 744. Isma'il, who also participated in his father's rebellion, lived in ascetic seclusion near Medina into the beginning of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
period (post-750) and the Umayyad caliph Umar II
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz ( ar, عمر بن عبد العزيز, ʿUmar ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz; 2 November 680 – ), commonly known as Umar II (), was the eighth Umayyad caliph. He made various significant contributions and reforms to the society, and ...
() reportedly considered appointing him his successor for his reputed piety. He was spared execution by the Abbasid governor of Medina Dawud ibn Ali Dawud may refer to:
* David in Islam
* Dawud (name)
* Dawud of Kanem, half-brother of the 14th-century Kanem emperor Idris I of Kanem
* An-Nasir Dawud, Kurdish ruler
* Askia Dawud, ruler of the Songhai Empire
* Mohammad Al-Dawud, Jordanian football ...
. Al-Ashdaq's daughter Umm Kulthum was also born to Umm Habib.
From his wife Sawda bint al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, the sister of Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr, al-Ashdaq had his sons Abd al-Malik and Abd al-Aziz and daughter Ramla. He was also married to A'isha bint Muti, the sister of Abd Allah ibn Muti
ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muṭīʿ al-ʿAdawī (died 692) was a leading Qurayshi of Medina and governor of Kufa for the anti-Umayyad caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr from April 685 until his ouster by the pro-Alid leader al-Mukhtar al-Thaqafi in August 68 ...
from the Banu Adi clan of Quraysh, who bore his sons Musa and Imran. From his Kalbite wife Na'ila bint al-Furays he had a daughter, Umm Musa. The latter was married to the son of Yazid I, Abd Allah al-Uswar. He also had children from two '' ummahat awlad'' (concubines), one of whom bore his sons Abd Allah and Abd al-Rahman and the other his daughter Umm Imran.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * {{Authority control 689 deaths 7th-century Arabs 7th-century executions by the Umayyad Caliphate Umayyad dynasty Generals of the Umayyad Caliphate Umayyad governors of Medina People of the Second Fitna Umayyad governors of Mecca